ethanol enzyme inhibitor
Thus as ethanol is added less methanol can bind to alcohol dehydrogenases active sites. Ethanol Corrosion Inhibitor Because ethanol is a single highly polar organic molecule that is completely soluble in water its performance can differ from traditional hydrocarbon fuels that contain numerous organic molecules.
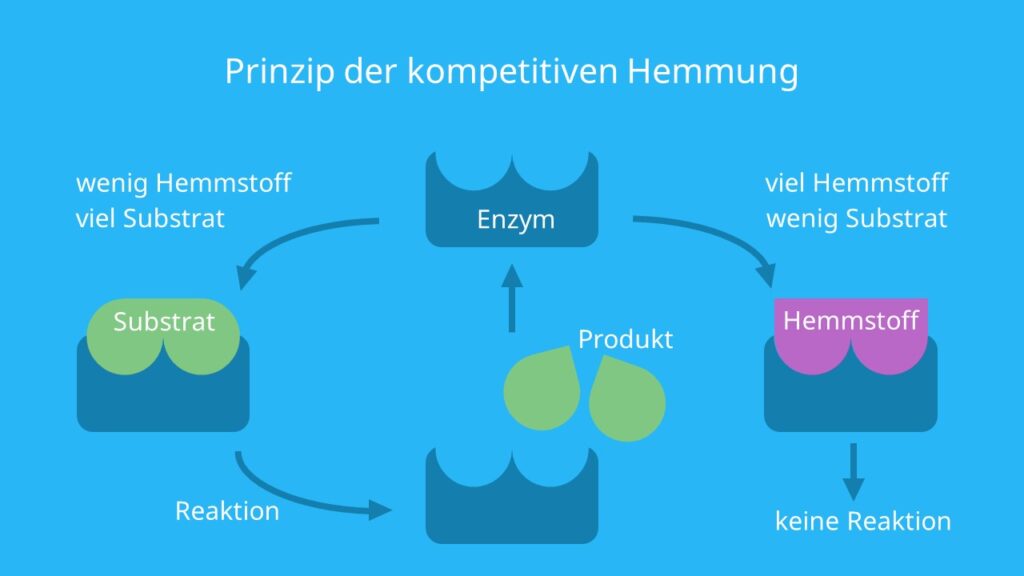
Kompetitive Hemmung Einfach Erklart Prinzip Mit Video
Plapp used the tight binding of this inhibitor to complex with YADH in a study of its crystal structure 12.
. 14 19-hete is an inhibitor of 20-hete a broadly active signaling molecule eg. The ethanol extract of tempuyung leaves Sonchus arvensis L has ACE inhibition activity on IC 50 of 4671 μgmL and IC 50 of captopril as a drug reference of 126 μgmL. Ethanol the compound found in alcoholic beverages.
We also found that. These enzyme inhibitors can attach to active areas and halt or inhibit further activity. Enzyme Inhibition Activities of Ethanol Extracts from Germinating Rough Rice Oryza sativar L June 2013 Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition 426.
Enzyme inhibitors can exist naturally and are implicated in the regulation of metabolism. Estimates were made of the dissociation constant for trifluoroethanol from the enzyme-NAD-trifluoroethanol complex in the range pH6-10. Therefore the amount of enzyme inhibition depends upon the inhibitor concentration substrate concentration and the relative.
Enzyme inhibitors are the substance which when binds to the enzyme reversibly or irreversibly decreases the activity of enzyme and the process is known as enzyme inhibition. Ethanol as an inhibitor in kinetic studies of the YADH mechanism. An ethanol corrosion inhibitor is a vital tool for fuel marketers.
Ethanol corrosion inhibitor dosage has long been difficult to control because there has not been an effective way to measure inhibitor content. However a competitive inhibition is usually reversible if sufficient substrate molecules are available to ultimately displace the inhibitor. Proper dosage prevents corrosion and protects fuel system components.
Furthermore we performed nelfinavir metabolism using LCMS. As a result handling storage use and performance of ethanol and ethanol-blended fuels can differ from conventional. This form of binding can be both reversible and irreversible.
However the in vivo ability and significance of 19-hete in inhibiting 20-hete has not been demonstrated see. Ethanol the molecule in the background is a competitive inhibitor for the enzyme Alcohol Dehydrogenase ADH It competes with methanol and other ethylene glycol for the active site of the enzyme. The stoppage of enzyme activity is referred to as enzyme inhibition.
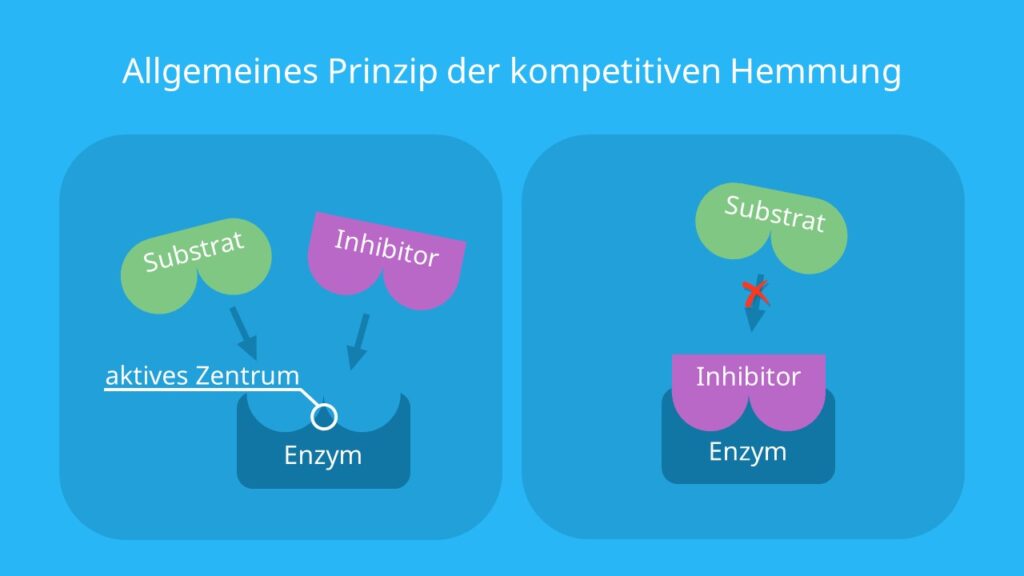
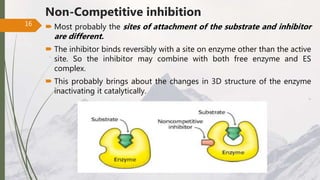
Reversible inhibition Competitive inhibition Noncompetitive inhibition 2. It competes with methanol for the active site. It is an essential way of maintaining homeostasis in the cell.
The results indicated that RNS inhibited the ethanol production of yeast cells with increased intracellular pyruvate content. Table of Contents Types of Enzyme Inhibition Competitive Inhibition. Formaldehyde is produced at a slower rate so the patient doesnt get as sick.
Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life in which substrate molecules are converted into products. It is very useful to treat alcohol poisonings which are common among those who ingest antifreeze and cheaper drinks. The inhibitors can impact both the substrate and the enzyme.
Ethanol is a competitive inhibitor of methanol to alcohol dehyrogenase. An enzyme inhibitor is a substance that binds with the enzyme and brings about a decrease in the catalytic activity of that enzyme. Thus as ethanol is added less methanol can bind to alcohol dehydrogenases active sites.
Formaldehyde is produced at a. Classical example of competitive inhibition 15. Ethanol is a competitive inhibitor of methanol to alcohol dehyrogenase.
Browse the articles related ethanol enzyme inhibitor. The inhibition was competitive with respect to ethanol in the ethanol-NAD reaction. These results suggest that ethanol facilitates binding of nelfinavir with CYP3A4.
Enzyme inhibitors are used to gain information about the shape of active site of enzyme and amino acids residues in active site. Here we use the inhibitory properties of the 222-trifluoroethanol binding to YADH in an experi-. Our Offerings Ethanol Corrosion Inhibitor Product Details.
An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult. Ethanol 20mM decreased the KD of nelfinavir by 5-fold 00410007 vs. Types of Enzyme inhibition This can be classified into the following types as 1.
Inhibition of yeast alcohol dehydrogenase by trifluoroethanol was studied at 25 degrees C and pH 6-10. This is called negative feedback which slows down the production line when the products start increasing. An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity.
First shown in 1971 ethanol inhibits retinol oxidation Mezey and Holt 1971 by human liver ADH as an alternate substrate with retinol for ADH. Enzyme inhibition occurs when a substance called an inhibitor binds to. NAD -dependent RA synthesis was shown to be inhibitable by ethanol in rat esophagus Shiraishi-Yokoyama et al 2003 or rat livercolon Parlesak et al 2000.
The inhibitor is stuck on the enzyme and prevents any substrate molecules from reacting with the enzyme. It competes with methanol for the active site. It constricts arterioles elevates blood pressure promotes inflammation responses and stimulates the growth of various types of tumor cells.
Similarly 20mM ethanol decreased the IC50 of nelfinavir by 3-fold 2605 vs. Enzymes in the metabolic pathway can be impeded by downstream products.

Enzyme Inhibition Types Purpose What Is Enzyme Inhibition Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Kompetitive Hemmung Einfach Erklart Prinzip Mit Video

717 Enzyme Inhibitor Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock

Metabolism Of Methanol To Formic Acid Alcohol Dehydrogenase Is The Download Scientific Diagram
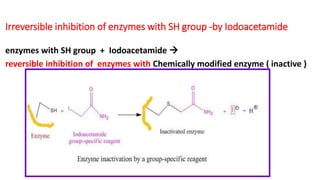
Enzymology Enzyme Inhibition Therapeutic Uses

Enzyme Inhibition Types Purpose What Is Enzyme Inhibition Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Enzyme Inhibition Types Purpose What Is Enzyme Inhibition Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Learn About Reversible Enzyme Inhibition Chegg Com

Selective Inhibition Of The C Domain Of Ace Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Combined With Inhibition Of Nep Neprilysin A Potential New Therapy For Hypertension Hypertension

Vitamin D Is Generally Responsible For The Absorption Of Calcium In Your Body Vitamin D Deficiency Can Result To T Nutrition Nutrition Awareness Levothyroxine

Alcohol Dehydrogenases An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Enzyme Inhibition Types Purpose What Is Enzyme Inhibition Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Dehydration Reaction To Form A Peptide Bond One Molecule Of Water Is Released Biochemistry Peptide Bond Chemistry

Enzyme Catalyst Active Site For Binding Reactants Stock Vector Illustration Of Biology Physics 216794778




Comments
Post a Comment